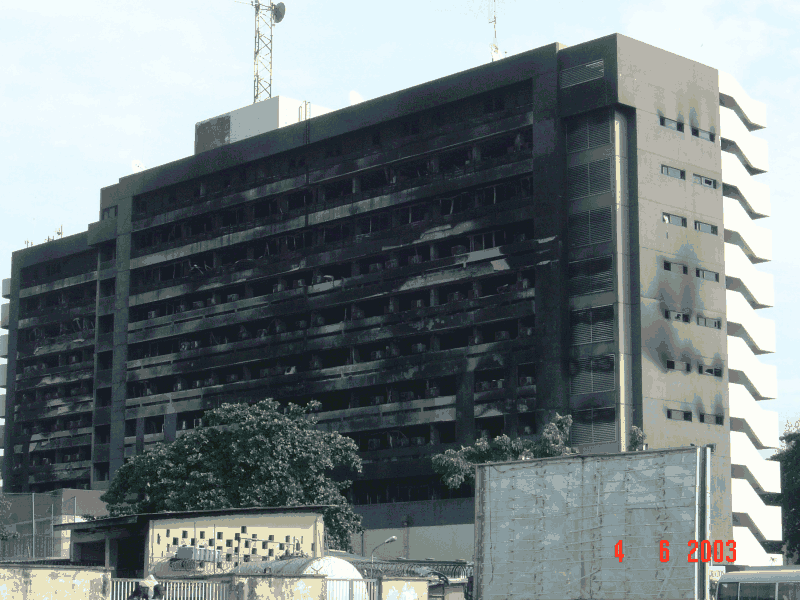
As data grows, backup and archive operations are becoming increasingly complex, and the customers are finding great gains in operational productivity from leveraging backup and archive reporting and service level-management disciplines. It is very difficult to improve on a process that isn’t measurable, so the first step is defining, monitoring and analyzing data on ongoing basis.
Added to data growth and complexity are government regulations and corporate governance projects that force backup and archive service level compliance.
Another challenge is that backup operations are typically run as a silo that has little or no alignment with business needs or understanding of how much backup recovery operation cost the business.
Benefits of Backup & Recovery
Organisations can gain a number of benefits by backing up important information.
- Prevent financial loss. Not being able to access vital sales information such as contacts and telephone numbers and leaving you with the inability to be able to generate sales, even if it's just for 24 hours can be catastrophic. This will not only impact upon revenue streams but can have a major impact upon cash flow.
- A backup and recovery system (as part of an effective disaster recovery programme) can prevent loss of credibility and goodwill.
- It will ensure that staff will continue to be paid especially if it impacts upon payroll and other key financial records.
- A backup and recovery system will eliminate the loss of important operational information such customer records and financial information.
- A backup and recovery system as part of a disaster recovery plan may ensure that legislation and compliance issues are adhered to. Many organisations have to comply with strict codes of conduct or face being fined. These include banks and other financial services organisations as well as legal practices and organisations that retain records.
- Implementing automatic backup software is a good idea because it means that there will be less need for human intervention or the potential of someone forgetting to take a backup.